 Neural Networks are Power Hungry
Neural Networks are Power Hungry
Advanced vehicles can use up to 30% of their battery just processing camera data. Typically, up to 10 cameras on board take images every second, each of which requires computational energy to identify nearby objects.
Solution: Create an independent information rich environment using passive RF-eye identification beacons to accurately determine position and identify nearby objects, thereby reducing computational requirements. Additionally, the RF-eye beacons teach the ML algorithms what these objects look like in all weather and lighting conditions.
-- medium.com
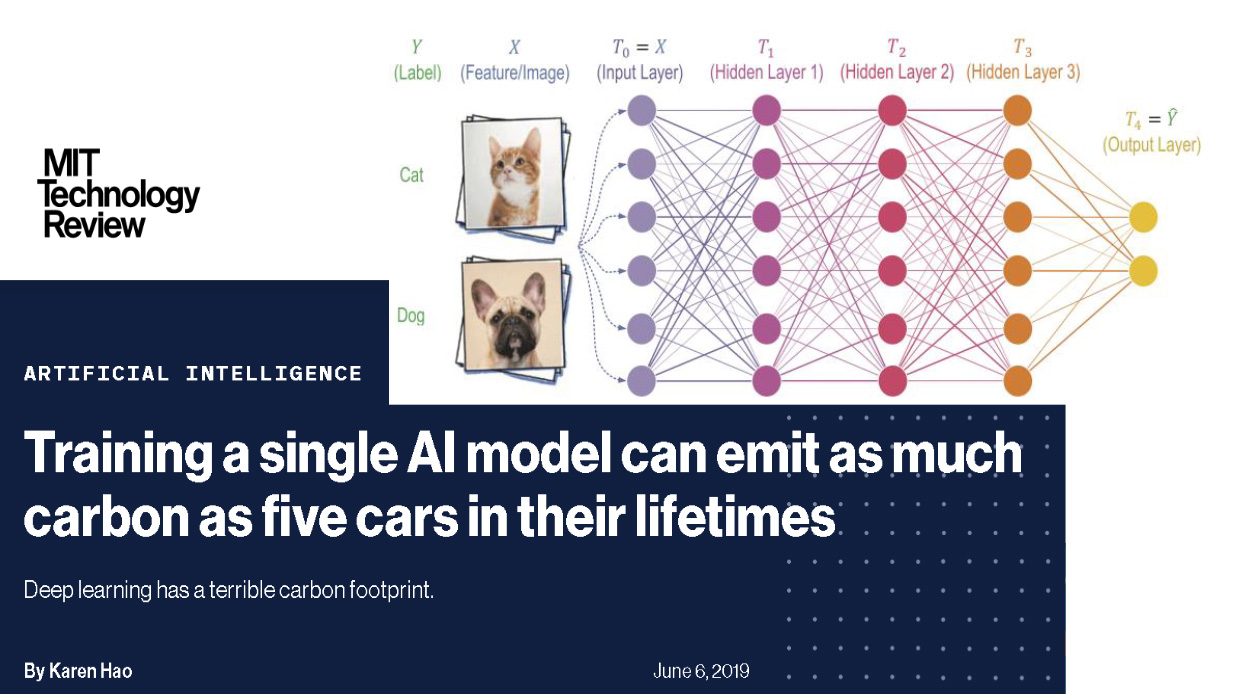 AI Training Consumes Massive Energy
AI Training Consumes Massive Energy
MIT experts estimate that each AI model emits as much carbon as five traditional automobiles in their entire lifetime, including manufacturing emissions. Many models are required to recognize each situation and object.
Solution: Objects on or near the road self-identify with RF-eye beacons, reducing the reliance of advanced vehicles on Deep Neural Network inferences to identify the objects, and reducing the need to create a model of every possible permutation of objects. Since RF-eye ‘tags’ objects, the AI algorithms learn from the images and tagged information to identify the objects in the future.
-- MIT Technology Review